Design Pattern - I
Definition of Design Pattern:
In software engineering, a software design pattern is a general reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem within a given context in software design. – WikiPedia.
Depends on abstract model but not implementation details.
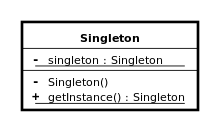
Singleton Pattern
Applicable scene:
We should use this design pattern when we will get trouble if we create many instances of a class. It’s enough for us to create only one instance of a class like Log Manager, utils, thread pool, cache manager, configure files manager and so on.
Targt:
We could use this pattern to restricts the instantiation of a class to one object.
An implementation of the singleton pattern must:
- ensure that only one instance of the singleton class ever exists
- provide global access to that instance.
There also have two different way to construct this pattern.
The first way:
|
|
The other way(Lazy Initialization):
|
|
Example in real project:
I used single pattern to implement the JedisPoolUtils class. This class helps me to manage a Jedis pool and binding lots of helpful functions in this tool class.
Recommened Article: how-to-correctly-write-singleton-pattern
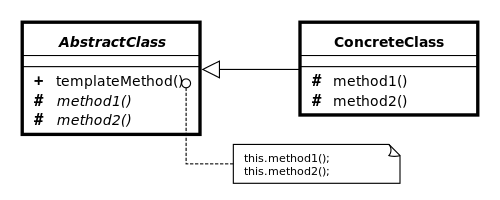
Template Method Pattern
Definition Of this pattern:
Template method pattern defines the program skeleton of an algorithm. It define a base class and allow the sub-class to override or implement some methods in the base class. The sub-class can redefine some special steps in the algorithm and don’t need to modify the architecture of the algorithm.
Applicable scene:
- Operations and procdure have common logical.
- Extract common codes into base class when you refactor your implementation.
- The target of algorithm is clearly.
Key elements to implement this pattern:
Abstract Base Class
a. Basic Methods. To different sub class, basic methods are same to them.
b. Abstract Methods or Callback Function. It know the principle but don’t know the detail of implementation.
c. Hook function. It only supply a default implementation in the base class, which can make sub-class more flexiable.
d. Template Method. According to the need of subclass (which means different needs of bussiness request),this method define an algorithm framework for all sub-class. It must be declared asfinal. Sub-class can replace theCall back functionandHook functioof base class but can’t replace another methods of base class.Concrete Sub Class
a. Implement the call back function which is inherited from base class.
b. The optional hook functions.
Prepare a base class and implement some basic common methods for different sub-class. Then, just leave some abstract methods for sub-class to implement. Finally, the template method function combine all element into a template method(algorithm).
Advantages:
- Encapsulation. This pattern encapsulate a algorithm framework and put the core part of the algorithm into a final method of base class. Lots of details are shielded.
- Reuse of codes. Avoid to write duplicate codes.
- Easy to maintain. All framework done :)
Disadvantages:
- Inheritance makes code coupling tightly.
Example in real project:
JedisPoolUtils.java
The inner class Executor is the base class of template method pattern and the different anonymous class is the sub-class which extend Executor and override the abstract method. getResult() is the template method.
Proxy
A proxy is a wrapper or agent object that is being called by the client to access the real serving object behind the scenes.
For the client, usage of a proxy object is similar to using the real object, because both implement the same interface.
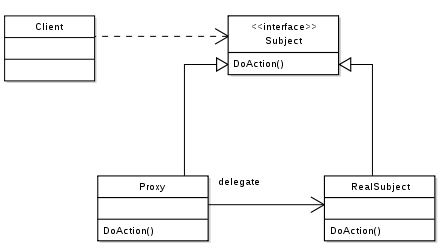
Static Proxy
The source code of the proxy class was created by programmer before compile. The static proxy which means it existed before the program run. It’s established that the relationship between proxy class and delegated class.
Dynamic Proxy
In contrast with static proxy, the dynamic proxy generates bytecode which requires Java reflection at runtime. With dynamic you don’t need to create the proxy class, which can lead to more convenience.
If you familar with MyBatis, you may be well known about ORM codes below there.
|
|
|
|
Generally, MyBatis also use dynamic proxy to generate an proxy instance for interface DAO. Everytime user call interface DAO, the action will be captured (by reflection) and transform to the proxy instance. You can find the proxy handler in the source code
Decorator
Lately, we have been talked about Proxy Pattern
作者: Jason Leaster
来源: http://jasonleaster.github.io
链接: http://jasonleaster.github.io/2017/04/16/Design-Pattern/
本文采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可